Researchers at Johns Hopkins College have provide you with a greater prosthetic hand that makes use of a hybrid design to fastidiously grip varied objects with simply the correct quantity of stress.
The robotic appendage combines inflexible and tender elements to imitate the pure construction of the human hand, in addition to a spread of sensors and a system to ship suggestions to the consumer’s nerves. In experiments, it efficiently picked up and manipulated 15 completely different objects, together with delicate stuffed toys, cardboard packing containers, pineapples, steel water bottles, and even a flimsy plastic cup stuffed with water – with out denting or damaging them.
“We wish to give folks with upper-limb loss the power to securely and freely work together with their setting, to really feel and maintain their family members with out concern of injuring them,” defined Sriramana Sankar, a biomedical engineering PhD scholar who led the analysis challenge. Sankar offered these findings in his first creator paper, which appeared in Science Advances this week.
Bionic Hand Grasps Like Human
The prosthetic system intently resembles a human hand, with 5 articulating fingers made utilizing tender rubber-like polymers, and a inflexible 3D-printed skeleton. Three layers of bioinspired tactile sensors enable it to correctly grasp and distinguish between a variety of objects. The fingers have air-filled joints which may be managed with the forearm’s muscular tissues.
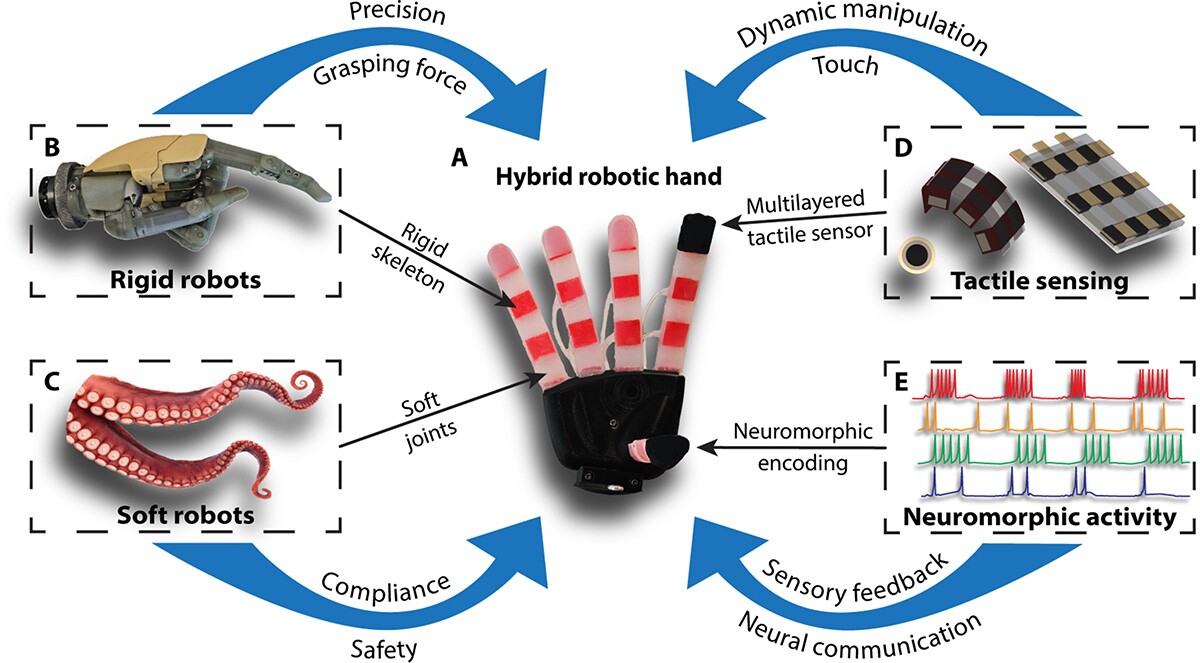
“The sensory info from its fingers is translated into the language of nerves to offer naturalistic sensory suggestions by way of electrical nerve stimulation,” Sankar mentioned. That is due to machine studying algorithms which focus the indicators from the sensors earlier than they’re directed again to nerves within the consumer’s physique – much like different prostheses.
These indicators bridge the mind and nerves, permitting the hand to react to what it is touching. This method allows a extra intuitively usable robotic hand that is a good bit extra like the actual factor than related efforts we have seen earlier than.
At present, the robotic hand may be managed utilizing EMG indicators, that are historically utilized by folks with upper-limb loss to manage myoelectric prosthetic arms. A US$150 gesture-control system known as the Myo Armband picks up and classifies the EMG indicators, and the hand positions are despatched to an Arduino microcontroller for pneumatic actuation of the robotic hand.
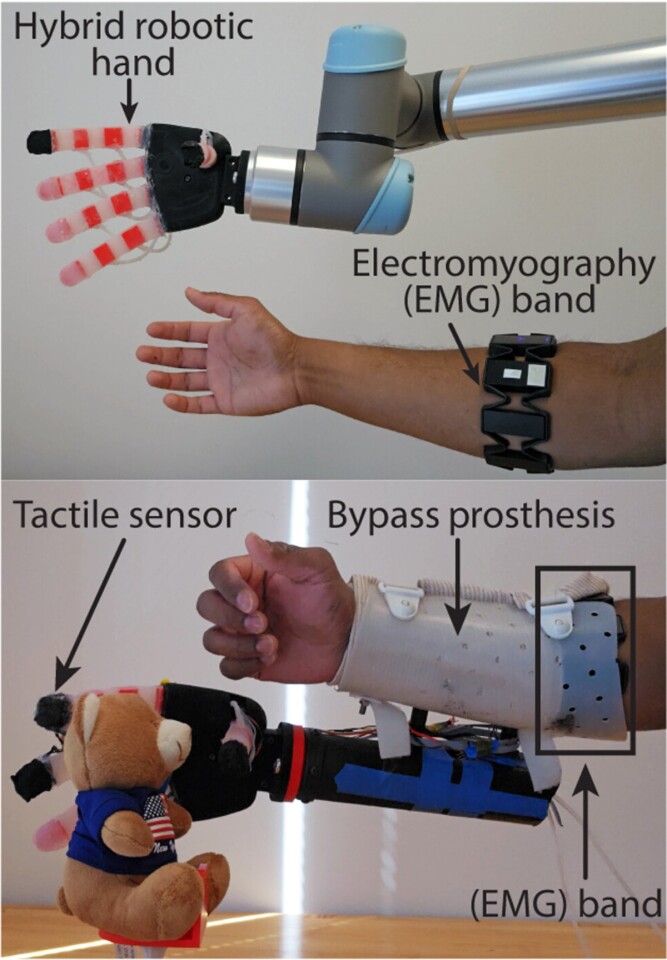
“When you’re holding a cup of espresso, how are you aware you are about to drop it?” mentioned Nitish Thakor, who directed the analysis. “Your palm and fingertips ship indicators to your mind that the cup is slipping. Our system is neurally impressed – it fashions the hand’s contact receptors to provide nerve-like messages so the prosthetics’ ‘mind,’ or its pc, understands if one thing is scorching or chilly, tender or onerous, or slipping from the grip.”
That goes a good bit additional than earlier efforts we have seen within the development of prosthetics. Final 12 months, scientists in Italy offered a technique to detect the temperature of objects a prosthetic hand got here in touch with. And approach again in 2021, a joint challenge between MIT and Shanghai Jiao Tong College demonstrated a prosthetic hand that exactly inflates particular person fingers made from a tender elastomer to understand objects and ship tactile suggestions.
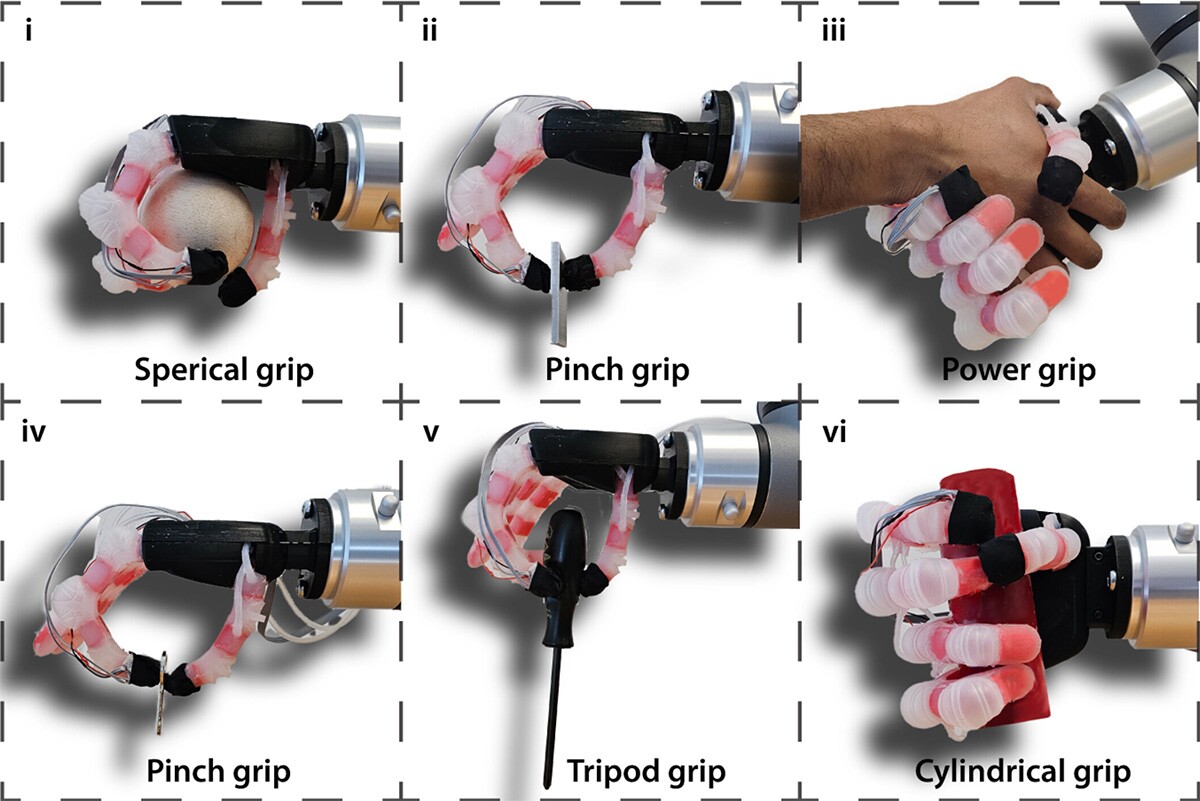

This new hand may unlock extra exact, natural-feeling prostheses for amputees – and in addition allow higher dexterity for humanoid robots tasked with dealing with delicate gadgets round your private home, and on the meeting line to construct extra bots.
The staff will proceed to develop this system by exploring the addition of stronger grip forces, extra sensors, and better high quality supplies.
Supply: Johns Hopkins College
xfbml : true, version : 'v3.3' }); };
(function(d, s, id){
var js, fjs = d.getElementsByTagName(s)[0];
if (d.getElementById(id)) {return;}
js = d.createElement(s); js.id = id;
js.src = "https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/sdk.js";
fjs.parentNode.insertBefore(js, fjs);
}(document, 'script', 'facebook-jssdk'));
[ad_2]

